Inheritance in Java
Expert View
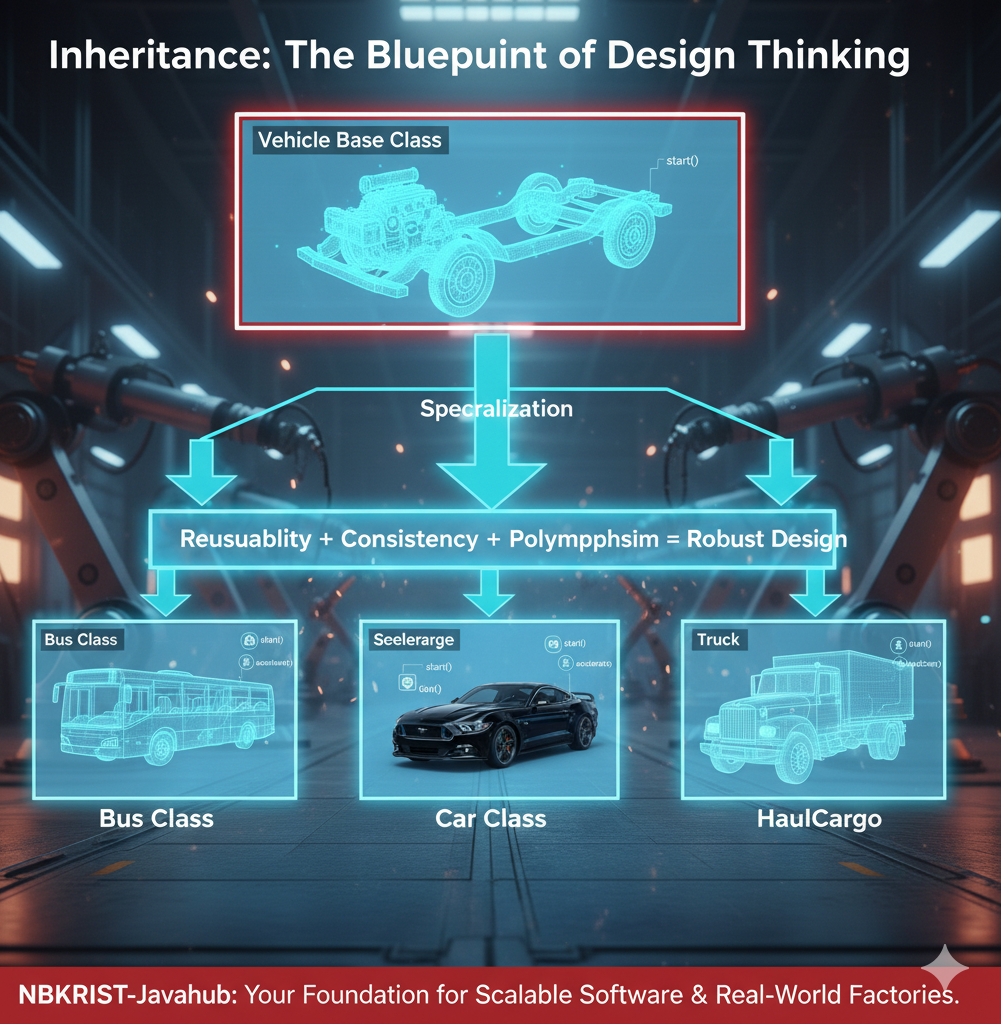
According to my experience, inheritance is not just a concept — it's the blueprint of
design thinking in Object-Oriented Programming.
Think of building a modern manufacturing system: you don’t rebuild every vehicle from scratch — you start with a
Vehicle base class and then specialize into Car, Bus, or
Truck.
This principle of specialization and generalization forms the foundation of scalable software
and real-world factories alike.
Inheritance drives reusability, consistency, and runtime polymorphism — the
three pillars of robust design.
My advice to every student: *Experiment, visualize, and build mini hierarchies in Java.* Watch how a simple
class structure can model complex manufacturing lines at NBKRIST’s Innovation Labs we have in our college. 🚀
1. Introduction
Inheritance allows a new class to derive properties and behavior from an existing class. It’s like how every new vehicle model inherits standard safety and design features from its parent blueprint in an automotive factory.

NBKRIST Vehicle starting...
Car driving smoothly...
2. Process of Inheritance
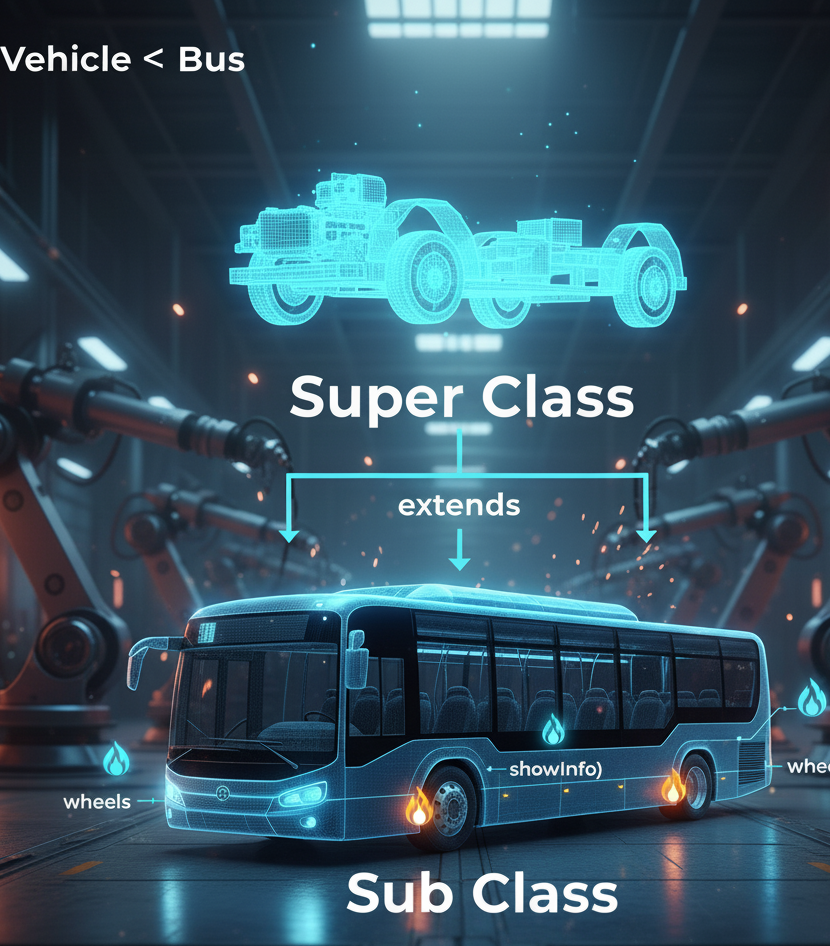
In Java, inheritance is implemented using the extends keyword. The subclass (child) inherits
accessible members from the superclass (parent), forming a “is-a” relationship.
NBKRIST Bus with 4 wheels.
3. Types of Inheritance
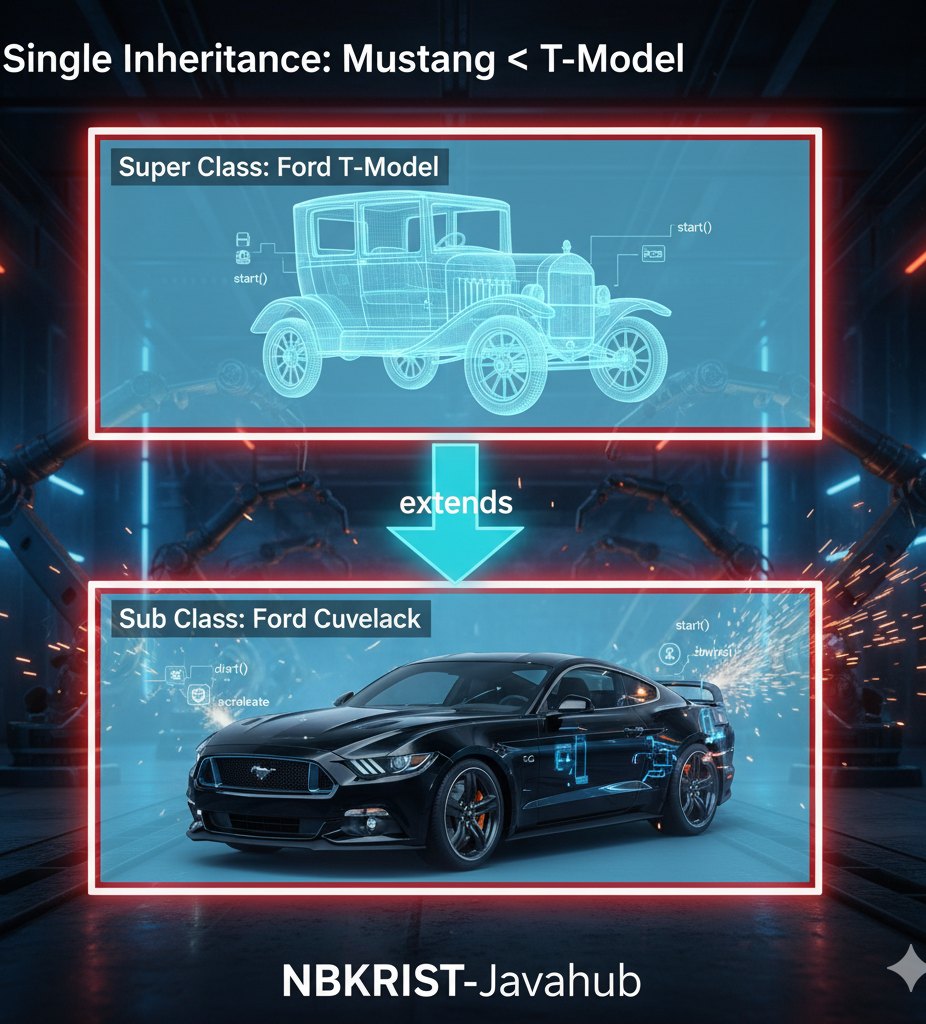
- Single:👉 A subclass inherits properties and behaviors from a single parent class. Car extends Vehicle.
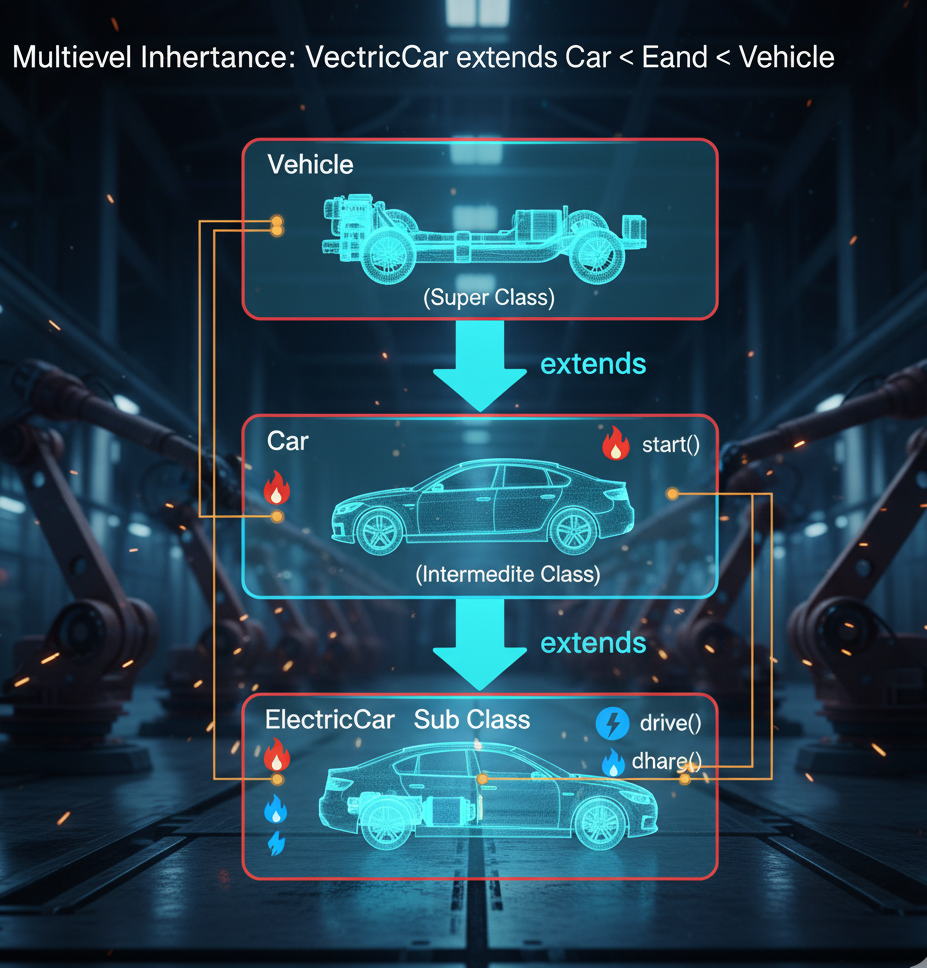
- Multilevel:👉 A class is derived from another derived class, forming a multi-layered chain. ElectricCar extends Car extends Vehicle.
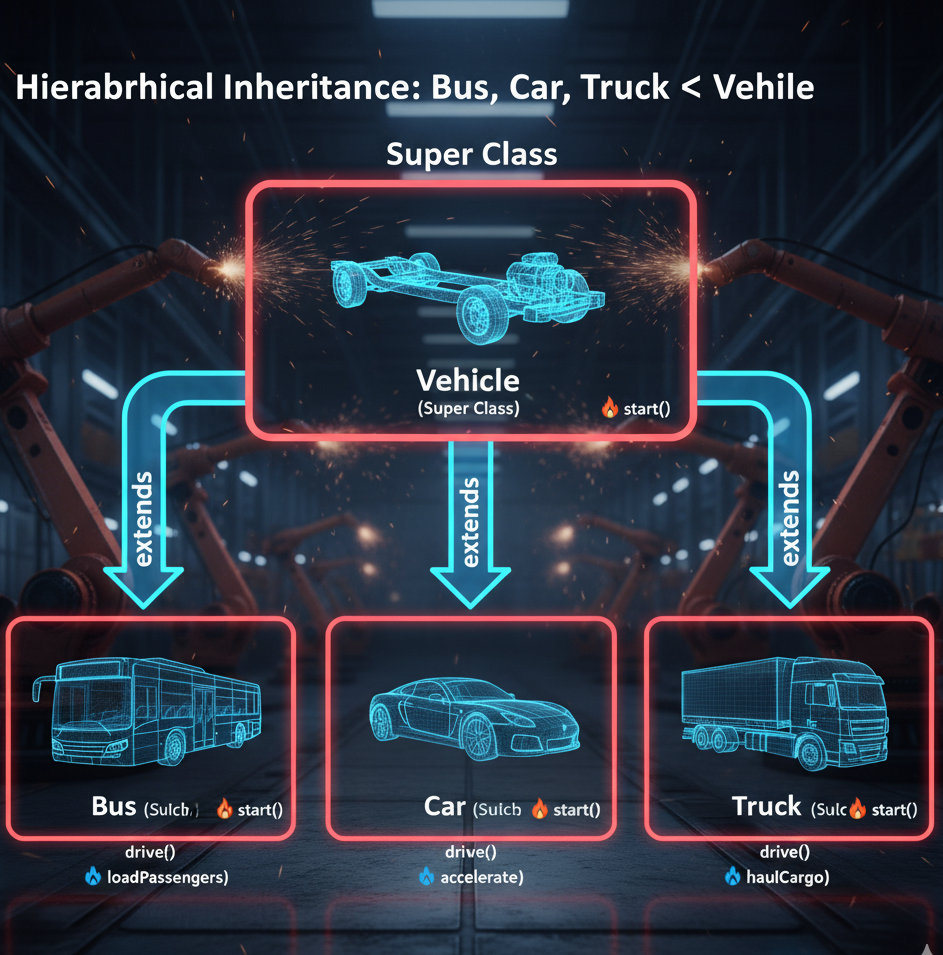
- Hierarchical:👉 Multiple subclasses inherit from the same parent class, sharing its common features. Bus, Car, and Truck all extend Vehicle.
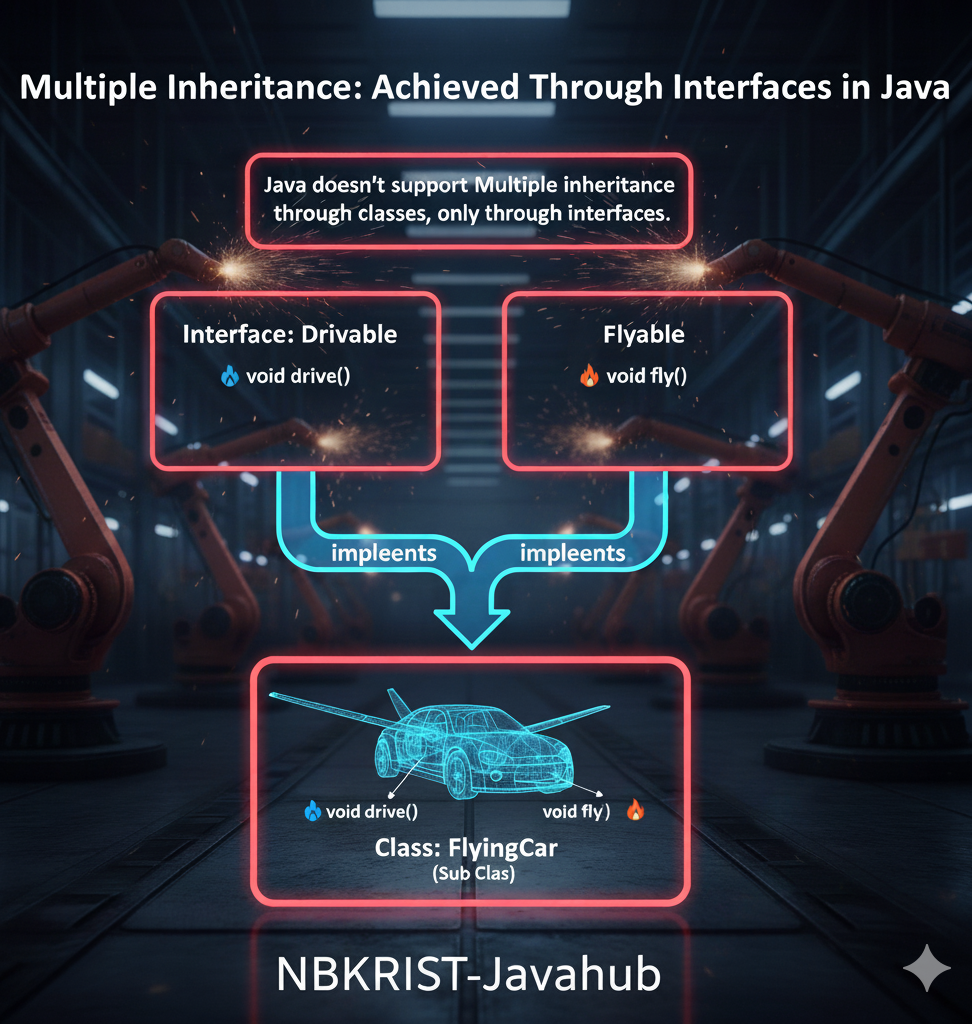
- Multiple:A class implements multiple interfaces to inherit behavior from multiple sources. Achieved through Interfaces in Java. class SmartCar implements GPS, Engine
4. Universal Superclass – Object Class
Every class in Java implicitly inherits from the Object class — much like every machine in a
factory follows universal operational protocols. This class provides methods such as equals(),
toString(), and hashCode().

NBKRIST Vehicle Model: Bus-XL
toString() to give meaningful representations
to your objects — especially in debugging and logging.
In Java, a superclass reference variable can hold a reference to any of its subclass objects. Since Object is the universal superclass of all classes in Java, it can refer to an instance of any class, making it a generic reference type within the language’s inheritance hierarchy.
Object base= new Vehicle("BUS-XXL");// correct
very high-level form of polymorphism!!! or Universal polymorphism through Object upcasting.
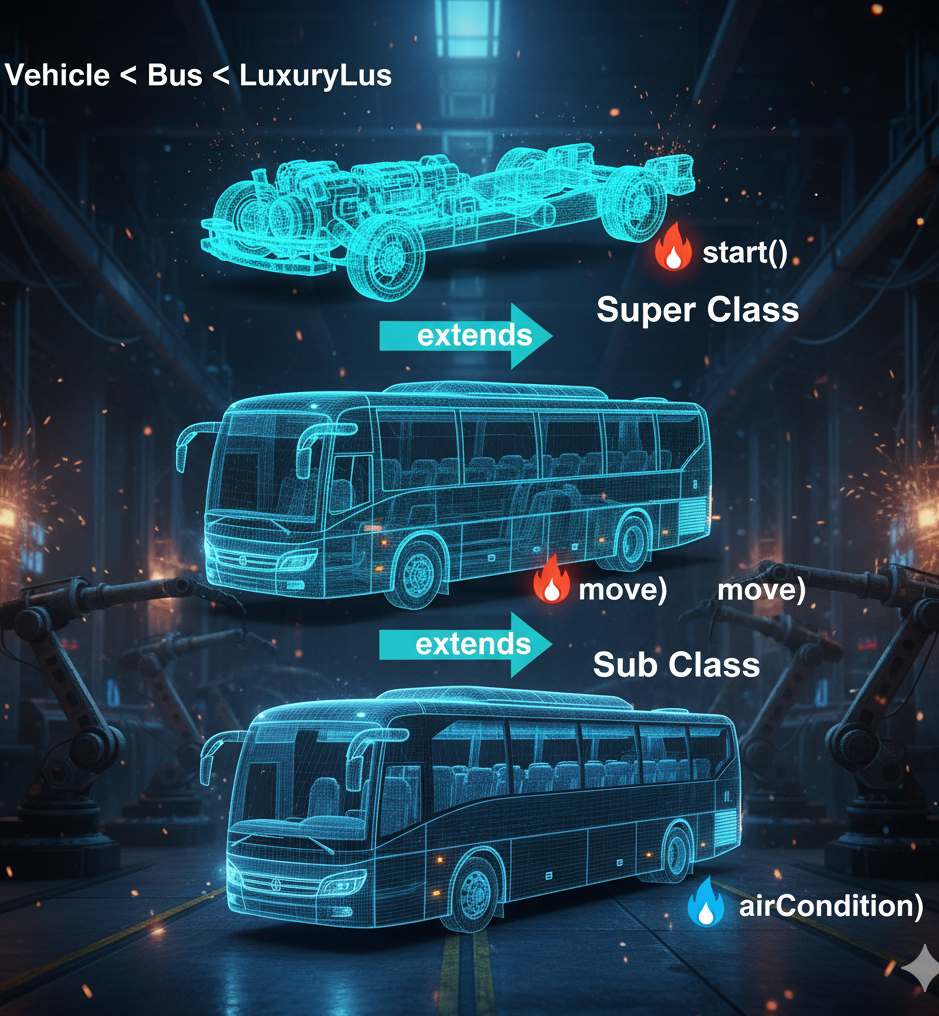
5. Multilevel Inheritance
Multilevel inheritance represents a layered evolution — for instance, a Bus inherits from Vehicle, and a LuxuryBus inherits from Bus.
NBKRIST Vehicle starting...
Bus moving...
AC running...
6. Application of Keyword super
The super keyword lets a subclass access its superclass members — ideal for refining inherited
behavior or invoking the parent constructor.
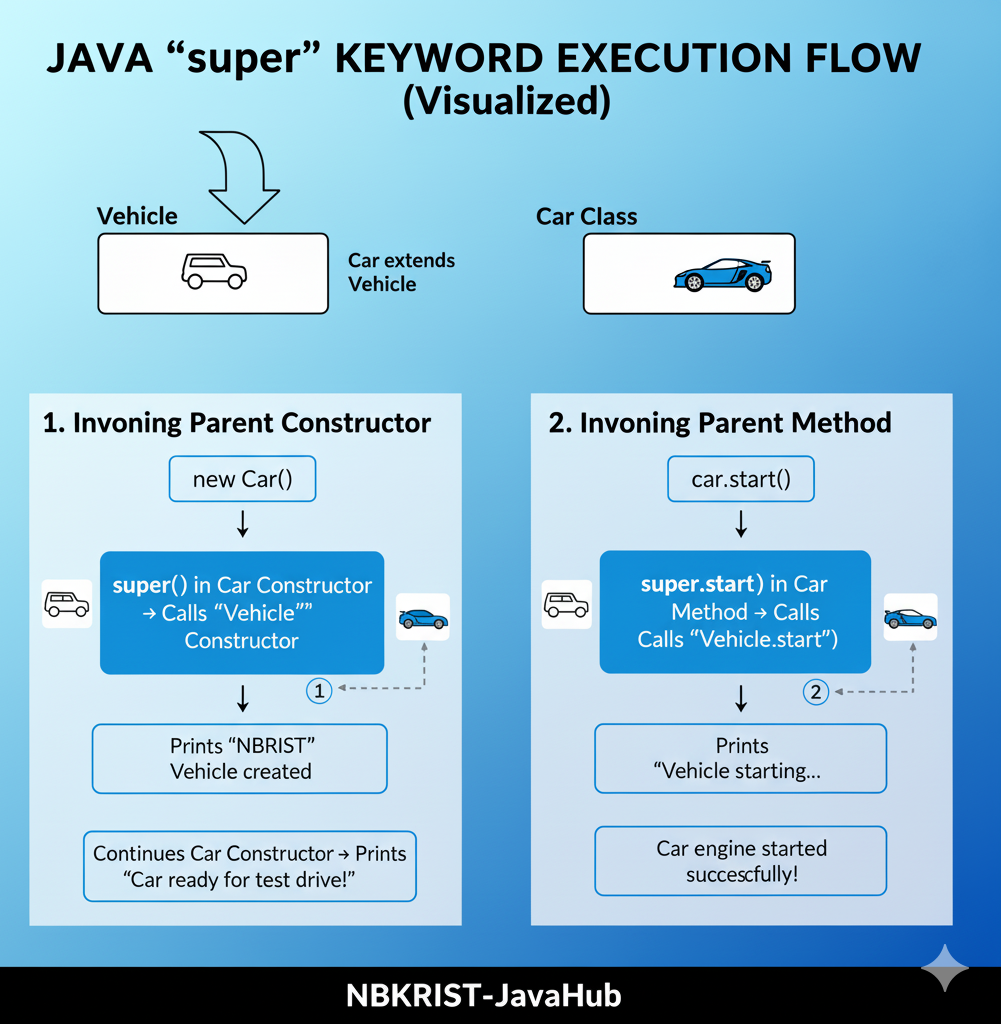
NBKRIST Vehicle created
Car ready for test drive!
Vehicle starting...
Car engine started successfully!
super() wisely to ensure the correct initialization
flow in complex hierarchies.As the super keyword plays a super-important role in Java inheritance, I’ve developed a dedicated page with detailed explanations and examples for each use of super. You’re encouraged to explore it after reading this page. Become Super
7. Constructor Method and Inheritance
Constructors are not inherited but invoked in a sequence from parent to child using super().
This ensures proper initialization from general (Vehicle) to specific (Car).

NBKRIST Vehicle built
Car assembled
SportsCar tuned for performance
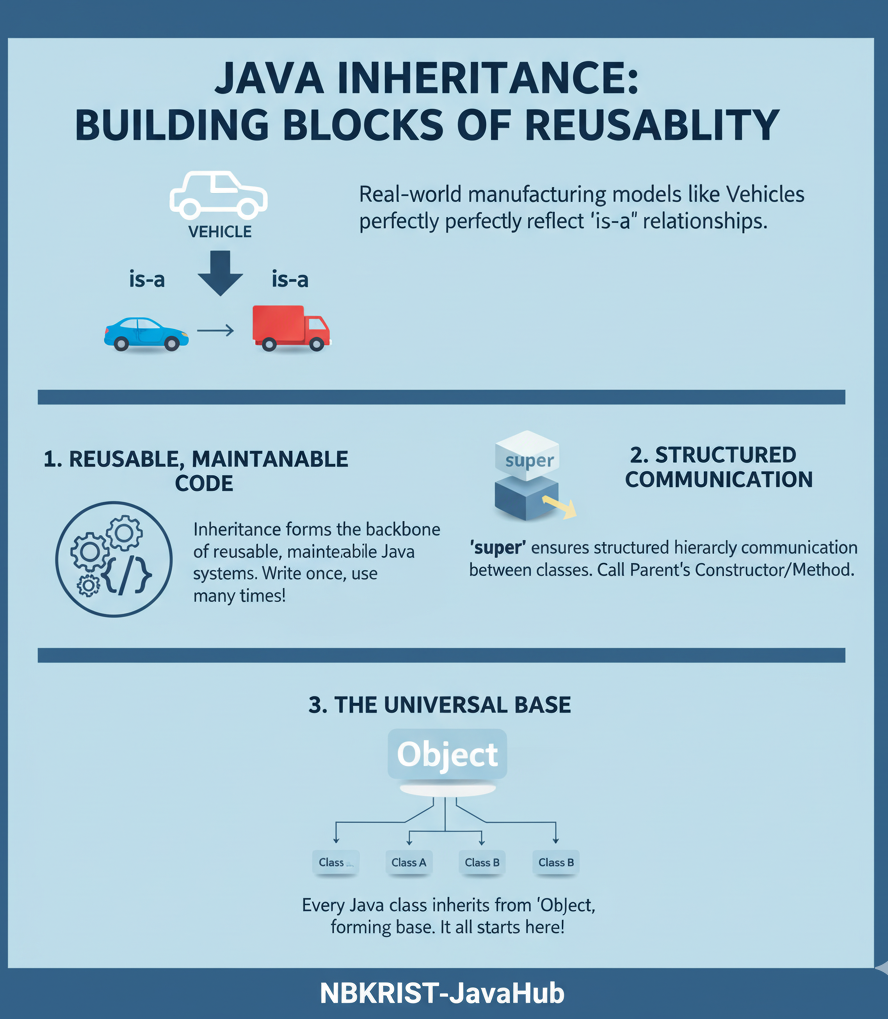
🔑 Key Takeaways
- Inheritance forms the backbone of reusable, maintainable Java systems.
- Real-world manufacturing models like Vehicles perfectly reflect “is-a” relationships.
superensures structured hierarchy communication between classes.- Every Java class inherits from
Object, forming the universal base. - Practice by building your own Vehicle hierarchy — make NBKRIST proud of your code!